Alexandru Rap: Research Interests: Previous work
Multi-Component Aerosol-Cloud Parameterisations for Global Climate Modelling
The project, funded by the UK Met Office
Hadley Centre, focused on improving the
parameterisation of aerosol-cloud interactions for global climate modelling. The other people involved in the project
were Prof. Mike Smith (Principal Investigator)
and Dr. Sat Ghosh.
A few results from our parameterisation from Rap et al. (2009), JAS and Ghosh et al. (2007), Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc.:
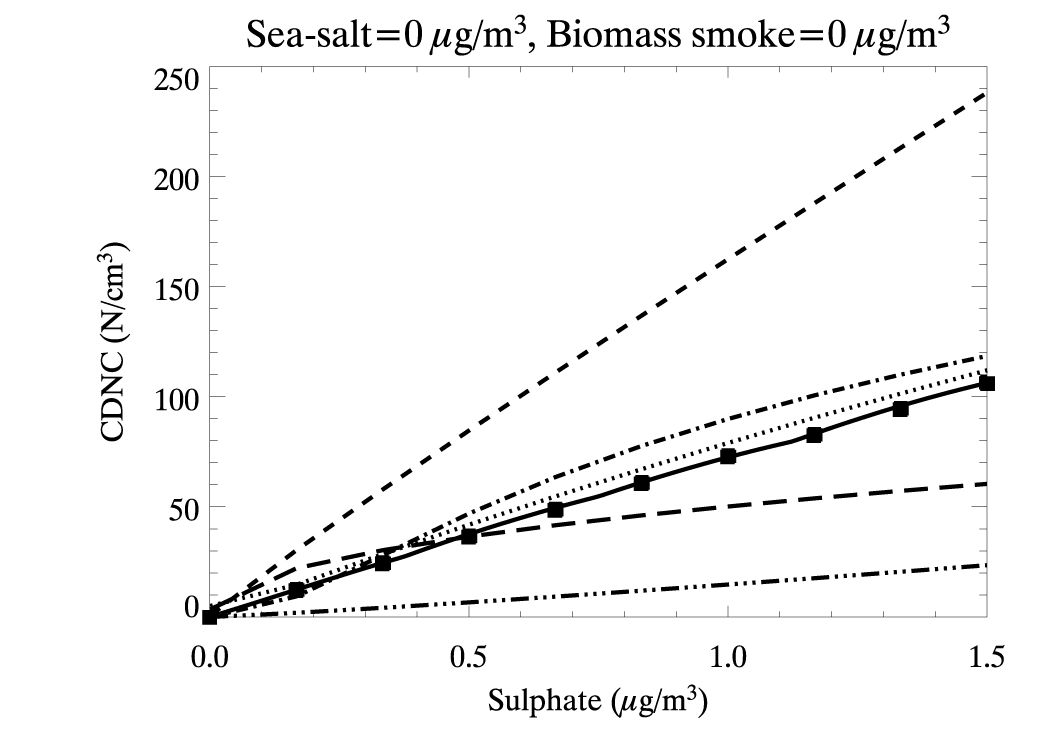
CDNC values as a function of sulphate aerosol mass concentration predicted by the model runs (solid black squares) and the following parameterizations: new scheme (solid), JRS94 (dotted), BL95 (short dashed), GN00 (dashed dotted), MD02 (dashed triple dotted), and QB05 (long dashed). This case considers fixed aerosol mass loadings of 0 ug m-3 sea salt and 0 ug m-3 biomass smoke.
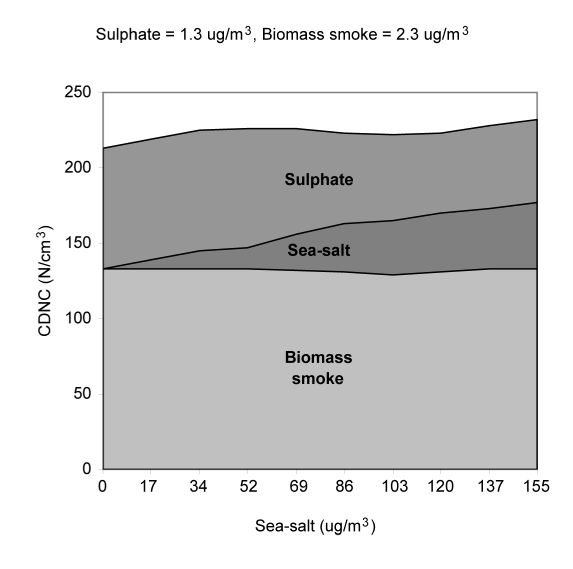
CDNC values predicted by the model to nucleate from the three aerosol species as a function of sea-salt aerosol mass concentration. This case considers fixed aerosol mass loadings of 1.3 ug m-3 sulfate and 2.3 ug m-3 biomass smoke.
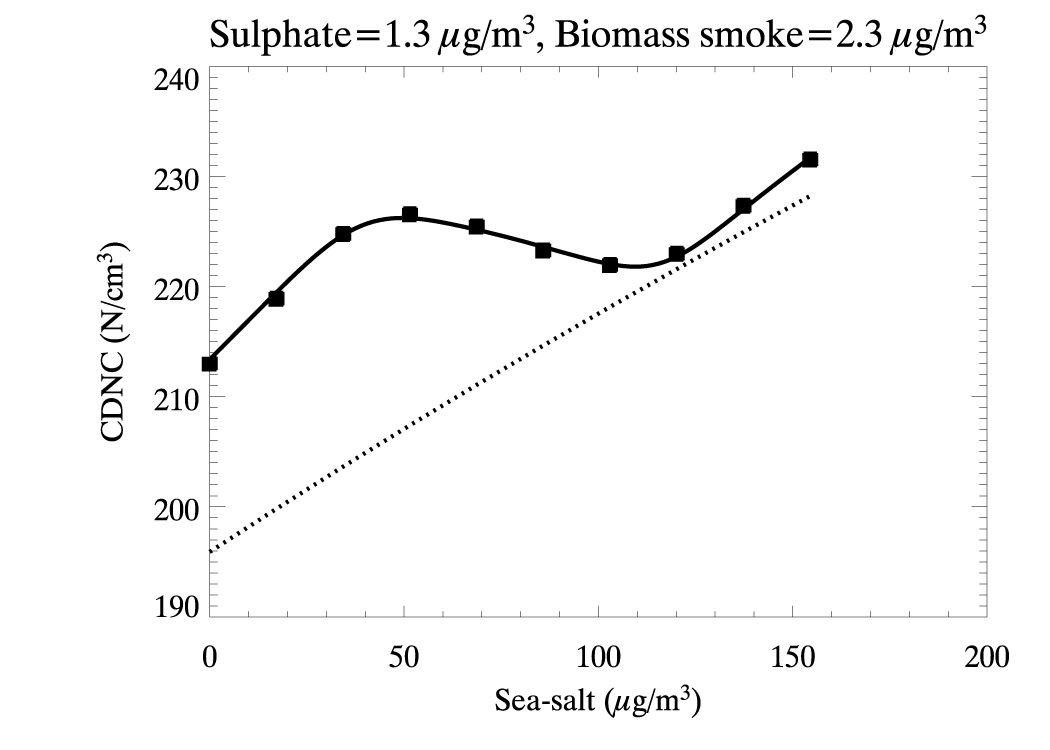
CDNC values as a function of sea-salt aerosol mass concentration predicted by the model runs (solid black squares), the new parameterizations scheme (solid line), and the JRS94 parameterization (dotted). This case considers fixed aerosol mass loadings of 1.3 ug m-3 sulfate and 2.3 ug m-3 biomass smoke.
As a PhD student in the Institute for Atmospheric Science, School of Earth and Environment, University of Leeds, I worked with Dr. Xianyun Wen and with Dr. Lionel Elliott, Professor Derek B. Ingham and Dr. Daniel Lesnic (Department of Applied Mathematics).
My main interest has been concentrated on inverse contaminant fluid flow problems.
The shortest definition of inverse problems describes them as discovering the cause from a
known result. Inverse problems are of an interdisciplinary nature
and arise in almost all research fields of science and
engineering. The main objective of my research as a PhD student
has been to extend the range of applications of the Boundary
Element Method (BEM) and the Dual Reciprocity
Boundary Element Method (DRBEM) for solving some inverse
problems related to water pollution. The inverse
problems considered in my research require the determination of
the location and strength of point sources of pollution (inverse
source problems) or boundary conditions for some hostile
part of the boundary (Cauchy problems). During
my research I have addressed these problems by developing a
series of efficient algorithms which combine the BEM and DRBEM
with regularisation techniques, such as Tikhonov
regularisation, Truncated Singular Value
Decomposition (TSVD) or an iterative procedure based on
a Sequential Quadratic Programming (SQP) method.
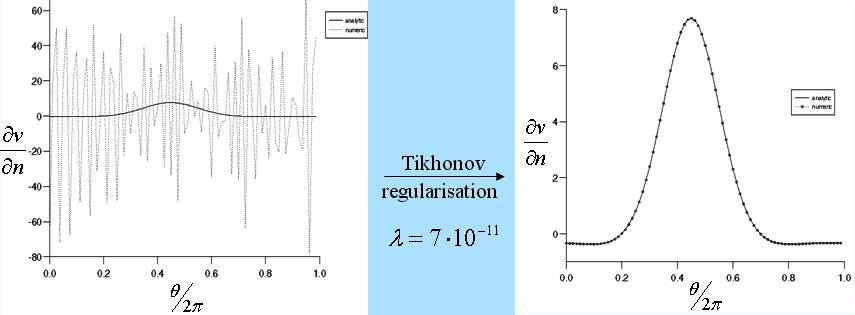
Work published in Rap et al. (2004), Rap et al. (2006), Rap et al. (2007), and Rap (2010).

| 


